- US inflation measured by the change in the Consumer Price Index printed 3.2% on a yearly basis in July.
- The reading came below market expectations of 3.3%.
- While inflation is a positive factor that typically drives Bitcoin value higher, the current situation where the US Fed is reducing liquidity is different, and the impact is largely uncertain.
The US Consumer Price Index (CPI), an economic indicator that is considered a measure of inflation, largely influences US Dollar dynamics and could help market participants predict the direction in which risk assets like Bitcoin and altcoin prices are headed.
The US Bureau of Labor Statistics reported a 3.2% increase in inflation, on a yearly basis, in July. This reading came slightly below the market’s expectation of 3.3%, and the impact on Bitcoin price is largely uncertain.
Also read: Breaking: US CPI inflation increases to 3.2% vs. 3.3% expected
Bitcoin traders likely to scale up their exposure to risk assets
With the July US CPI data slightly below consensus, there is scope for the Federal Reserve to stay hawkish for a while, introducing downside volatility to risk assets like Bitcoin.
Given the spike in Bitcoin’s social volume over the past thirty days, it is likely that more traders scoop up BTC at discounted prices and await forward-looking macroeconomic indicators to signal a recovery in the cryptocurrency’s price.
Moreover, the CPI is one of the most widely used measures of inflation and the July reading signals that the Federal Reserve has been effective in reducing liquidity in the system. The impact of inflation as an economic indicator, on Bitcoin, is rather uncertain with BTC price ranging below the $30,000 post the July data release.
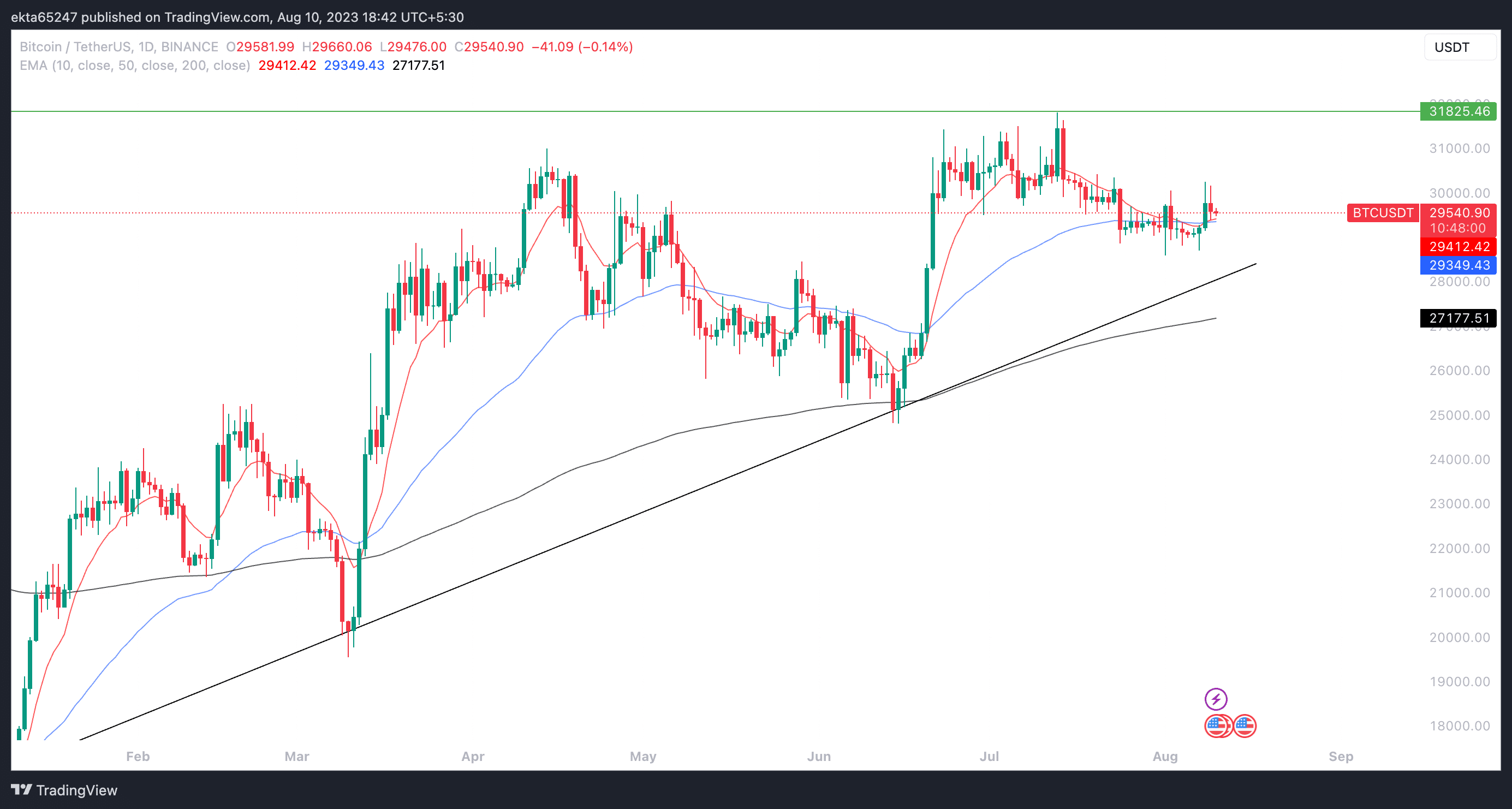
Bitcoin price is currently above its three long-term Exponential Moving Averages (EMAs), 10, 50 and 200-day at $29,530, $29,349 and $27,177 respectively.
BTC/USDT one-day price chart on Binance
Inflation has driven Bitcoin to its all-time highs previously. BTC price rallied to the $65,000 level during the period of Fed’s monetary policy expansion in 2021. During this period there was a consistent increase in inflation and this aided BTC’s comeback through a massive price rally.
Inflation FAQs
Inflation measures the rise in the price of a representative basket of goods and services. Headline inflation is usually expressed as a percentage change on a month-on-month (MoM) and year-on-year (YoY) basis. Core inflation excludes more volatile elements such as food and fuel which can fluctuate because of geopolitical and seasonal factors. Core inflation is the figure economists focus on and is the level targeted by central banks, which are mandated to keep inflation at a manageable level, usually around 2%.
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) measures the change in prices of a basket of goods and services over a period of time. It is usually expressed as a percentage change on a month-on-month (MoM) and year-on-year (YoY) basis. Core CPI is the figure targeted by central banks as it excludes volatile food and fuel inputs. When Core CPI rises above 2% it usually results in higher interest rates and vice versa when it falls below 2%. Since higher interest rates are positive for a currency, higher inflation usually results in a stronger currency. The opposite is true when inflation falls.
Although it may seem counter-intuitive, high inflation in a country pushes up the value of its currency and vice versa for lower inflation. This is because the central bank will normally raise interest rates to combat the higher inflation, which attract more global capital inflows from investors looking for a lucrative place to park their money.
Formerly, Gold was the asset investors turned to in times of high inflation because it preserved its value, and whilst investors will often still buy Gold for its safe-haven properties in times of extreme market turmoil, this is not the case most of the time. This is because when inflation is high, central banks will put up interest rates to combat it.
Higher interest rates are negative for Gold because they increase the opportunity-cost of holding Gold vis-a-vis an interest-bearing asset or placing the money in a cash deposit account. On the flipside, lower inflation tends to be positive for Gold as it brings interest rates down, making the bright metal a more viable investment alternative.
Like this article? Help us with some feedback by answering this survey: